 http://www.ted.com/index.php/talks/d...your_fate.html
http://www.ted.com/index.php/talks/d...your_fate.html
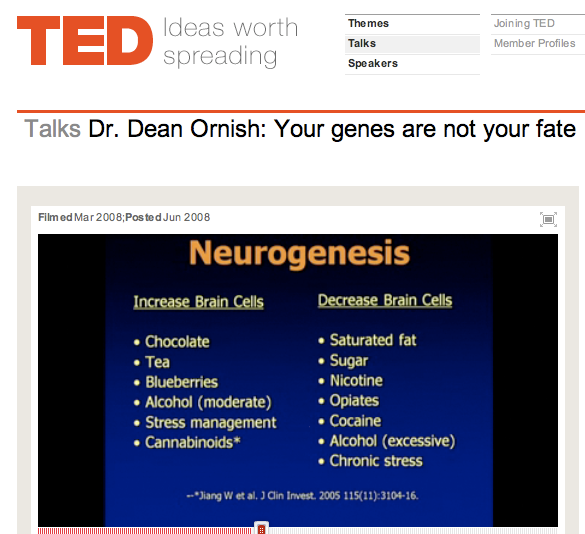
Cannabinoids promote embryonic and adult hippocampus neurogenesis and produce anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects.
J Clin Invest. 2005 Nov;115(11):3104-16. Epub 2005 Oct 13.
From the Abstract: The hippocampal dentate gyrus in the adult mammalian brain contains neural stem/progenitor cells (NS/PCs) capable of generating new neurons, i.e., neurogenesis. Most drugs of abuse examined to date decrease adult hippocampal neurogenesis, but the effects of cannabis (marijuana or cannabinoids) on hippocampal neurogenesis remain unknown. This study aimed at investigating the potential regulatory capacity of the potent synthetic cannabinoid HU210 on hippocampal neurogenesis and its possible correlation with behavioral change. We show that both embryonic and adult rat hippocampal NS/PCs are immunoreactive for CB1 cannabinoid receptors, indicating that cannabinoids could act on CB1 receptors to regulate neurogenesis. This hypothesis is supported by further findings that HU210 promotes proliferation, but not differentiation, of cultured embryonic hippocampal NS/PCs likely via a sequential activation of CB1 receptors, G(i/o) proteins, and ERK signaling. Chronic, but not acute, HU210 treatment promoted neurogenesis in the hippocampal dentate gyrus of adult rats and exerted anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects. X-irradiation of the hippocampus blocked both the neurogenic and behavioral effects of chronic HU210 treatment, suggesting that chronic HU210 treatment produces anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects likely via promotion of hippocampal neurogenesis.
AND
In The Neuroscientist vol 13, no. 2, 109-114 (2007)
"The Endocannabinoid System and Neurogenesis in Health and Disease"
From the abstract: The endocannabinoid system exerts an important neuromodulatory function in different brain areas and is also known to be involved in the regulation of neural cell fate. Thus, CB1 cannabinoid receptors are neuroprotective in different models of brain injury, and their expression is altered in various neurodegenerative diseases. Recent findings have demonstrated the presence of a functional endocannabinoid system in neural progenitor cells that participates in the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation. In this Research Update, the authors address the experimental evidence regarding the regulatory role of cannabinoids in neurogenesis and analyze them in the context of those pathological disorders in which cannabinoid function and altered neuronal or glial generation is most relevant, for example, stroke and multiple sclerosis. NEUROSCIENTIST 13(2):109—114, 2007.